First, we see what is DNS recon actually means, DNS recon is the process of gathering as much as information about the DNS Server (Convert domain name into IP Address and vice versa) used by the web application or host.
DNS recon provides various sensitive information like IP Addresses, Name Servers, Mail Servers, Hosts details, Virtual Hosts, DNS records, etc.
Now we will see how to conduct DNS Recon using various tools.
host <Domain Name> - it provides the IPv4 or IPv6 addresses of the domain
Now we will see how to conduct DNS Recon using various tools.
1. Host
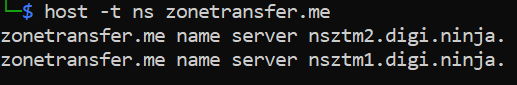
host -t ns <Domain Name> - it provides the Name Server details of the domain
Here -t is the type of DNS record.
host -t mx <Domain Name> - it provides mail server details

Now we will see how to conduct a Zone Transfer attack using the host command.
So, Zone transfer is a process of copying the DNS database or zone file from the primary DNS server to the secondary DNS server.
To conduct the zone transfer attack first, we have to identify the name server.
host -t ns <domain name> - provides the name server details

Now we will list all the domains using the AXFR query.
Here -t is the type of DNS record.
host -t mx <Domain Name> - it provides mail server details
Now we will see how to conduct a Zone Transfer attack using the host command.
So, Zone transfer is a process of copying the DNS database or zone file from the primary DNS server to the secondary DNS server.
To conduct the zone transfer attack first, we have to identify the name server.
host -t ns <domain name> - provides the name server details
Now we will list all the domains using the AXFR query.
host -l <domain name> <name server>
2. Dig
Now we will see how to conduct DNS recon using the dig command, dig works in the form of Question and Answer.
dig <Domain Name> - by default, dig provides the A record information
dig <Domain Name> -t ns - it provides the Name server information
-t - is the type of query
dig <Domain Name> -t mx - it provides the mail server information
Similarly, we can set -t as CNAME, AAAA, or any other DNS query.
Now we see how to conduct a Zone Transfer attack using the dig command.
First, identify the name server by using it.
dig <Domain Name> -t ns
Then we have to list all the domains using the AXFR query.
dig axfr <Domain Name> @<Name Server>
3. NSlookup
nslookup <Domain Name> - by default, nslookup provides the IP Address of the Domain Name
To identify the name server first, enter nslookup, then set type=ns, then enter the domain name.
To identify the mail server information, set type=mx, then enter the domain name.
Now we see how to conduct a Zone Transfer attack using the dig command.
First, identify the name server, then set the server as a name server and type as any.
Now enter ls -d <Domain name> to list all the domains.

